基于动态交换的核磁共振分子探针——通向分子层面原位多组分检测技术
赵延川研究员
中国科学院上海有机化学研究所
时间:2024年5月31日(星期五)10:30
地点:思明校区卢嘉锡楼202报告厅
厦门大学谱学分析与仪器教育部重点实验室
2024年5月21日
报告人简介:
赵延川,中国科学院上海有机化学研究所有机氟化学重点实验室研究员。2007年本科毕业于吉林大学,2012年博士毕业于中国科学院上海有机化学研究所。之后在美国麻省理工学院化学系从事博士后研究;期间,在美国伊利诺伊香槟分校进行交流访问。2017年5月加入中国科学院上海有机化学研究所,任课题组长。获国家高层次人才-青年项目资助。
研究兴趣:课题组致力于有机功能分子设计、合成及应用。发展了基于分子识别的色谱核磁共振分析方法,检测中无需分离、无需标记、实时在线地得到类似于色谱峰的检测信号,精确对应复杂体系中的各个组分。发展了新型仿生离子受体—Calix[4]trap (杯芳烃离子阱),其具有目前报道最高的K+/Na+选择性,可以通过动力学和热力学两种机制高选择性地分离金属离子并能够实现离子的可控传输。
Dr. Yanchuan Zhao is a Professor in the Key Laboratory of Organofluorine Chemistry at the Shanghai Institute of Organic Chemistry, CAS. He received his bachelor's degree from Jilin University in 2007 and his Ph.D. degree from Shanghai Institute of Organic Chemistry (SIOC), CAS in 2012. After that, he did postdoctoral research in the Department of Chemistry of the Massachusetts Institute of Technology; during this period, he spent one month at the University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign as a visiting scholar. In May 2017, he joined SIOC as a group leader. Dr. Zhao's research interests include fluorinated functional molecules and materials, supramolecular chemistry, and the self-assembly of macromolecules. Special emphasis is on the use of a confined environment to modulate the thermodynamic and kinetics of dynamic recognition systems. Dr. Zhao has authored more than 60 articles in international refereed journals, such as J. Am. Chem. Soc., Angew. Chem. Int. Ed., Chem. Rev., JACS Au, Cell Reports Phy. Sci., Anal. Chem., and Macromolecules.

报告摘要:
对真实复杂样品的快速准确检测在食品安全监测、生产过程控制、疾病诊断及生物机制研究等方面都有重要的应用。目前色谱分析技术在复杂体系检测中应用最广,但其基于分离,相对耗时,难以满足高通量及原位检测需求。利用光谱及化学传感方法可以避免分离,实现原位快速分析,但分析准确性易受杂质的干扰并且难以获取样品精确的组分信息。色谱方法的“高精确性”和光谱/化学传感方法的“原位及快速性”是分析领域一直追寻的优良检测特性,然而却难以整合在同一种分析技术中。本报告将介绍一种基于核磁共振氟谱和动态可逆交换的化学传感方法,检测中无需分离、无需标记、实时在线地得到类似于色谱峰的检测信号,精确对应复杂体系中的各个组分(图1)。该方法独特的检测能力为研究复杂系统中的多组分相互作用及演化规律提供了有力工具。同时,利用具有独特手性空腔的含氟核磁共振探针可以对醇、酰胺、环醚、亚砜等大量结构不同的手性化合物进行快速分析并确定其绝对构型,为手性相关研究领域提供新的高通量检测手段。
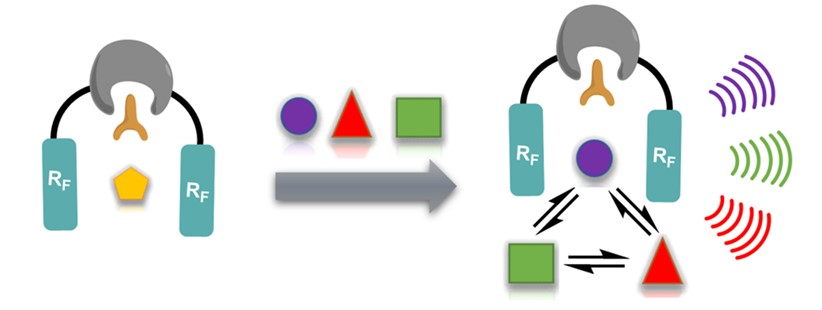
图1 识别赋能色谱核磁检测技术
参考文献
[1] Gu, G.; Xu, Z.; Wen, L.; Liang, J.; Wang, C.; Wan, X.; Zhao, Y. Chirality Sensing of N-Heterocycles via 19F NMR. JACS Au 2023, 3, 1348–1357.
[2] Li, H.; Xu, Z.; Zhang, S.; Jia, Y.; Zhao, Y. Construction of Lewis Pairs for Optimal Enantioresolution via Recognition-Enabled “Chromatographic” 19F NMR Spectroscopy. Anal. Chem. 2022, 94, 2023–2031.
[3] Xu, Z.; Gu, S.; Li, Y.; Wu, J.; Zhao, Y. Recognition-Enabled Automated Analyte Identification via 19F NMR. Anal. Chem. 2022, 94, 8285–8292.
[4] Wen, L.; Meng, H.; Gu, S.; Wu, J.; Zhao, Y. Toward Nanomolar Multi-Component Analysis by 19F NMR. Anal. Chem. 2022, 94, 8024–8032.
[5] Li, Y.; Wen, L.; Meng, H.; Lv, J.; Luo, G.; Zhao, Y. Separation-Free Enantiodifferentiation with Chromatogram-like Output. Cell Reports Phys. Sci. 2020, 1, 100100.